Borrowers seeking respite from elevated interest rates may face potential disappointment, as financial markets suggest that rates will likely remain high for an extended period.
The decline in money market rates in 2024 suggests that the prolonged period of near-zero interest rates following the Great Financial Crisis is unlikely to be repeated. This is due to inflationary pressures and increased government spending, which are expected to persist.
This situation poses a potential challenge for public and private borrowers who have previously secured loans at lower interest rates and have yet to experience the complete effects of the rapid interest rate increases implemented by the central bank over the past two years.
In recent weeks, traders have significantly increased their expectations for substantial interest rate reductions in the upcoming year. This shift in sentiment is driven by the deceleration of inflation and a more accommodative stance from the U.S. Federal Reserve.
The anticipation of a decrease of at least 1.5 percentage points in interest rates in the United States and Europe has positively impacted bond and equity markets.
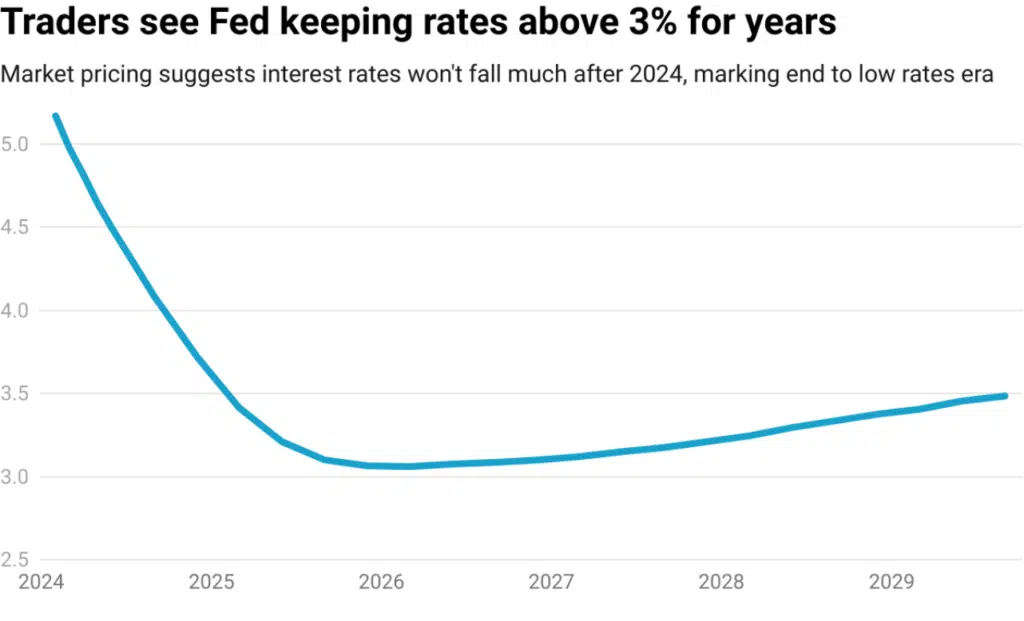
According to money market pricing, the Federal Reserve is anticipated to decrease its key interest rate to approximately 3.75% by the conclusion of 2024. However, it is projected to decline to around 3% by the end of 2026 and subsequently increase to about 3.5%.
The current situation significantly differs from the period after the global financial crisis, where interest rates remained nearly zero for most of the decade. It was only in 2018 that they gradually increased to a range of 2.25% to 2.50%.
The European Central Bank rates are anticipated to be around 2% by the end of 2026, compared to the current rate of 4%. This reduction, however, should not be interpreted as a signal of a potential revival of the unconventional approach of implementing negative rates, which was observed between 2014 and 2022.
The objective is to establish a policy that promotes standardization. According to Mike Riddell, a senior portfolio manager at Allianz Global Investors, the current monetary policy must be adjusted towards an accommodative stance.
According to economists, these expectations align with a situation where the ‘neutral’ interest rate, which has no impact on economic growth, has increased since before the COVID-19 pandemic.
The U.S. economy has managed to avoid a recession despite initial expectations due to aggressive policy tightening. This further strengthens the argument in favor of its resilience.
There is a possibility of increased inflation due to geopolitical tensions, reshoring, looser fiscal policy, and potential advancements in productivity through technologies like AI. These factors could raise the neutral rate, known as ‘R-star.’
The concept of the neutral rate is crucial for comprehending an economy’s capacity for growth and guiding a central bank’s decision-making regarding interest rate reductions in the future. While it is challenging to ascertain the neutral rate in real-time, it remains an essential factor in economic analysis.
Whether the neutral rate has experienced any changes is a subject of extensive discussion, and there are differing opinions regarding its potential increase.
Significantly, the market’s anticipated long-term interest rates surpass the Federal Reserve’s estimated rate of 2.5%. Some policymakers have even projected it to exceed 3%.
Within the euro area, European Central Bank (ECB) policymakers have indicated that the neutral interest rate is estimated to be 1.5% to 2%.
Idanna Appio, a former economist at the Federal Reserve who currently serves as a portfolio manager at First Eagle Investment Management, expressed skepticism regarding the extent of the change in R-star.
Appio is perplexed by the discrepancy between market pricing, which indicates expectations of sustained high-interest rates, and various indicators of inflation expectations, which suggest a potential return to central banks’ desired targets. According to her, it is premature to conclude that there has been an increase in productivity.
Predicting the direction of interest rates in the future is a challenging task, as market dynamics can sometimes lead to inaccurate forecasts.
However, borrowers need to exercise caution due to the expectations set by lenders, as they have become accustomed to and continue to reap the benefits of the historically low-interest rates observed in recent years.
According to Patrick Saner, the head of macro strategy at Swiss Re, corporates will have to seek new financing options at higher interest rates than the rates they had recorded in their financial records over the past five years.
A higher rates environment is essential, especially in corporate planning.